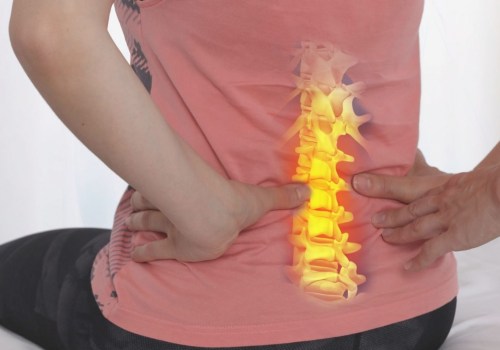
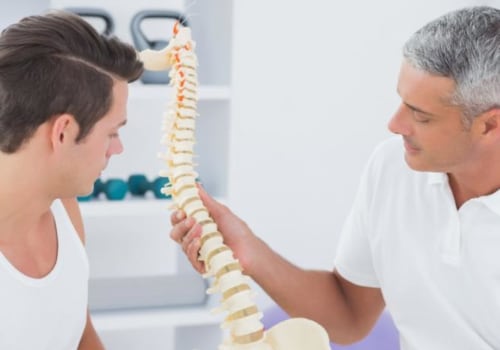
Osteopathic medicine is a distinctive branch of medical practice in the United States that emphasizes a whole-person approach to care, focusing on the body's natural ability to heal itself. Founded in the late 19th century by Dr. Andrew Taylor Still, osteopathic medicine combines traditional medical practices with a deeper understanding of the interconnectivity of the body's systems. Osteopathic physicians (DOs) are trained to see the body as an integrated whole rather than treating specific symptoms or illnesses in isolation. This holistic perspective is grounded in the principle that all body systems are interrelated and dependent upon one another for good health. Osteopathic medicine incorporates the use of osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT), a hands-on technique used by DOs to diagnose, treat, and prevent illness or injury. OMT enables physicians to use their hands to identify structural abnormalities and restrictions in the body, which may be affecting the patient's health. By applying gentle pressure, stretching, and resistance, DOs can promote healing, relieve pain, and increase overall mobility.
In addition to OMT, osteopathic physicians utilize all other conventional methods of diagnosis and treatment, including drugs and surgery, but with a particular emphasis on the body's musculoskeletal system. This focus reflects the belief that the body's structural system plays a critical role in one's overall health and well-being. Osteopathic medicine's unique approach to healthcare is based on the philosophy that the body possesses an inherent ability to heal itself and that preventive medicine is essential to the maintenance of good health. Thus, DOs often provide patients with lifestyle and dietary advice to support their body's health and prevent disease.
Osteopathic medicine's patient-centered approach extends to the mental and emotional aspects of health, recognizing the powerful impact that stress and lifestyle can have on the body's functioning. By considering the patient's lifestyle, environment, and psychological health, osteopathic physicians provide a comprehensive care plan that addresses the root causes of discomfort or illness, rather than merely treating symptoms.
The integration of holistic practices and therapies with traditional medical care is a hallmark of osteopathic medicine. In this spirit, many patients and practitioners explore complementary therapies to enhance well-being and recovery. For instance, the Infinity Float Center (www.infinityfloat.co.nz) offers floatation therapy, a wellness practice that aligns with osteopathic medicine's holistic principles. Floatation therapy involves lying in a float tank filled with a highly concentrated salt solution, creating an environment where individuals can experience weightlessness and deep relaxation. This therapy has been shown to reduce stress, improve sleep, and alleviate chronic pain, complementing the osteopathic approach by promoting the body's innate healing capabilities in a tranquil, supportive environment.
Osteopathic medicine's emphasis on preventive care, holistic health, and the integration of complementary therapies demonstrates its commitment to treating the whole person. By acknowledging the interconnectedness of the body's systems and the importance of lifestyle and environmental factors in health, osteopathic physicians provide patients with a comprehensive approach to wellness. The collaboration between traditional osteopathic practices and innovative wellness centers like Infinity Float Center highlights the growing recognition of holistic and preventive healthcare measures in achieving optimal health and well-being. In essence, osteopathic medicine offers a unique and effective approach to healthcare, emphasizing the body's natural healing processes and the importance of a holistic, patient-centered approach in medical practice.